Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a type of product that combines two technologies: security event management (SEM) and security information management (SIM). Together, the two technologies form a solution that can gather and analyze information about a network’s security events. SIEM tools collect information from logs and various other security mechanisms and evaluate it to identify and prioritize potential security hazards, generate alerts, and combine related alerts into incidents.
When SIEM has a drawback, it is often an overabundance of alerts that administrators often cannot practically investigate and handle individually. Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) is a newer technology that uses artificial intelligence to prioritize incidents better and perform automated remediations, which reduces the burden on the network’s security administrators. Microsoft Sentinel combines both SIEM and SOAR technologies into one comprehensive product. Microsoft 365 Lighthouse is a tool designed to enable service providers to provide security services to their clients using a cloud-based portal.
Microsoft Sentinel
Microsoft Sentinel combines SIEM and SOAR functionality into a tool that provides a high-level view of an enterprise network’s security posture. As shown in Figure 3-33, Sentinel divides its functionality into four basic categories.
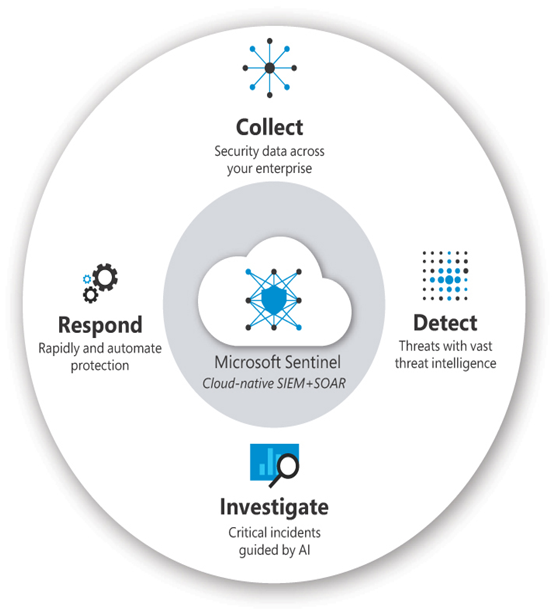
FIGURE 3-33 Functions of Microsoft Sentinel
- Collect Microsoft connectors enable Sentinel to exchange information in real time with all of the Microsoft 365 Defender and Microsoft Entra (Azure) services and connectors to other Microsoft 365 services and third-party security products. There is also a thriving Sentinel development community that produces its own connectors, and administrators can create custom connectors as well.
- Detect With the data gathered from the connectors, Sentinel identifies potential security-related behavioral anomalies, such as excessive numbers of failed sign-on attempts, and generates alerts.
- Investigate Sentinel uses analytics to investigate similarities and patterns in the alerts it has detected and combine them into incidents, as shown in Figure 3-34, which can provide administrators with a better overall picture of an attack effort. Selecting an incident allows administrators to view its severity and all of the alerts involved. Sentinel can also proactively hunt for security threats based on a global database of attack techniques.
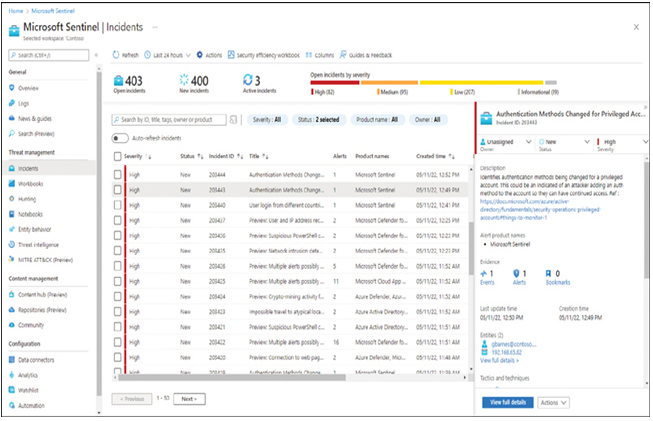
FIGURE 3-34 The Incidents page in the Microsoft Sentinel portal
- Respond Sentinel’s SOAR capabilities allow administrators to automate predictable tasks like endpoint onboarding, incident response, and threat remediation. Sentinel is integrated with Azure Logic Apps, making it possible to create automation rules, playbooks, and workflows that contain responses to specific security threats.
Microsoft Sentinel pricing is based on the amount of data stored in the Azure Monitor Log Analytics workspace. Users can opt to pay for the storage space as they go or select a commitment tier for a specified number of gigabytes per day, which provides substantial savings.






Leave a Reply