Category: Service Trust Portal
-

Priva rights requests-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365
Read More: Priva rights requests-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365In recent years, there has been legislation passed in many countries providing citizens with the right to request that organizations disclose any personal information about them that they possess. These might seem like simple requests to the requestor, but for an organization that maintains a large data store, locating all of the requested information concerning…
-

Auditing-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365
Read More: Auditing-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365Microsoft Purview includes auditing capabilities that log operations for many Microsoft 365 applications and services. Administrators can search the audit log directly from the Microsoft Purview portal, providing detailed information that can be useful during security, compliance, and legal investigations. Microsoft Purview can provide two levels of audit logging, as follows: FIGURE 3-49 The Audit…
-

Data-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365
Read More: Data-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365All the security functions applying to the other five Zero Trust criteria essentially protect the organization’s data—its most valuable resource. Administrators must consider the data’s security in all possible states: in-motion, at-rest, and in-use. Depending on the nature and sensitivity of the data, each state might require different security measures. Microsoft 365 supports tools that…
-

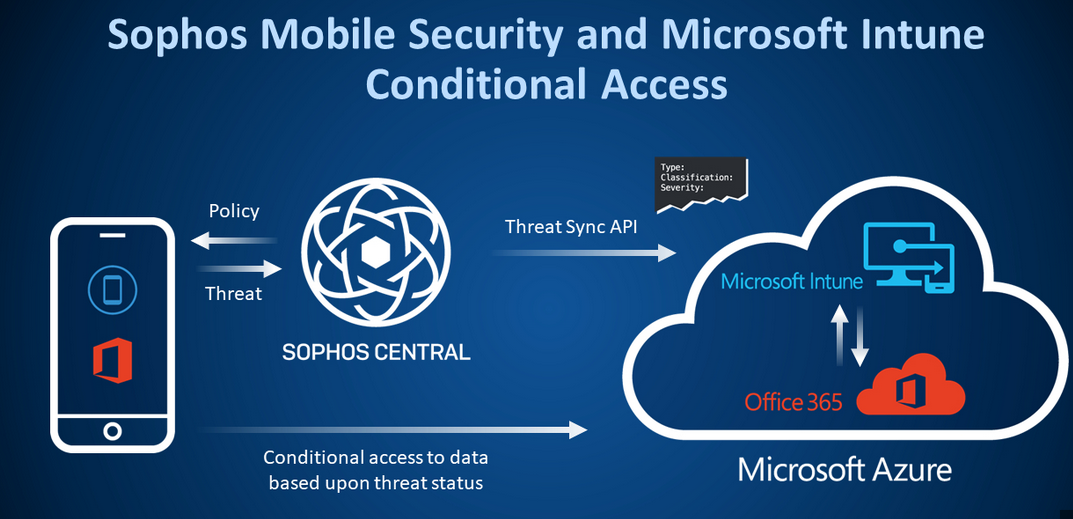
Endpoints-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365
Read More: Endpoints-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365An endpoint is any device that connects to the network from any location, whether the device belongs to the company, an employee, or a guest user. Zero Trust calls for security policies to be applied and enforced uniformly on endpoints of all types by tools such as Microsoft Intune, regardless of the users’ identities or…
-

Describe the Zero Trust model-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365
Read More: Describe the Zero Trust model-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365At one time, enterprise security could be considered a perimeter surrounding an organization. Data remained largely within the organization’s sites and could be protected from unauthorized access by firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), and physical barriers. Even when data began to be accessible beyond the organization using Internet websites and portable devices, the company still…
-

Microsoft 365 Lighthouse-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365
Read More: Microsoft 365 Lighthouse-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365Small- and medium-sized businesses often lack IT personnel with a sufficient security background to manage and monitor the network using the tools provided in Microsoft 365. This creates a market for managed service providers (MSPs) who can lend their security expertise to their clients to help them protect their networks. Microsoft 365 Lighthouse is a…
Search
Popular Posts
-
Anticipating threats-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365
Arguably, the most difficult part of the risk management planning process is trying to anticipate all the possible threats that could afflict the company’s data in the future. The three basic risk factors for the data—confidentiality, integrity, and availability—can be exploited in any number of specific ways, but the general threat categories are listed in…
-
Classifying users-Describe security, compliance, privacy, and trust in Microsoft 365
The third element of the digital estate that must be considered when creating a risk management plan is the people who actually access the data. Whether deliberately or inadvertently, users are a constant vulnerability—if not an actual threat—to the organization’s data. After quantifying the organization’s information assets and their value and inventorying the hardware used…